GPS
Echtzeit GPS 


Verbinden Sie ihr GPS-Gerät via COM-Schnittstelle d.h. Bluetooth mit ihrem Computer. Falls ihr GPS-Gerät über einen USB-Anschluss mit dem Computer verbunden ist, benötigen Sie eine Software wie z.B. GPSGate, welche die Daten an einen virtuellen COM-Port überträgt.
Das GPS-Gerät muss das NMEA 0183 Format senden.
![]() Stellen Sie sicher, dass das Koordinatensystem auf ihrem GPS-gerät auf WGS84 oder eine UTM-Zone eingestellt ist. Andernfalls kann OCAD die Daten nicht korrekt umrechnen und die Position um mehrere 100 Meter abweichen!
Stellen Sie sicher, dass das Koordinatensystem auf ihrem GPS-gerät auf WGS84 oder eine UTM-Zone eingestellt ist. Andernfalls kann OCAD die Daten nicht korrekt umrechnen und die Position um mehrere 100 Meter abweichen!
Wählen Sie Echtzeit GPS... aus dem Menü GPS. Der Dialog Echtzeit GPS Einstellungen erscheint.
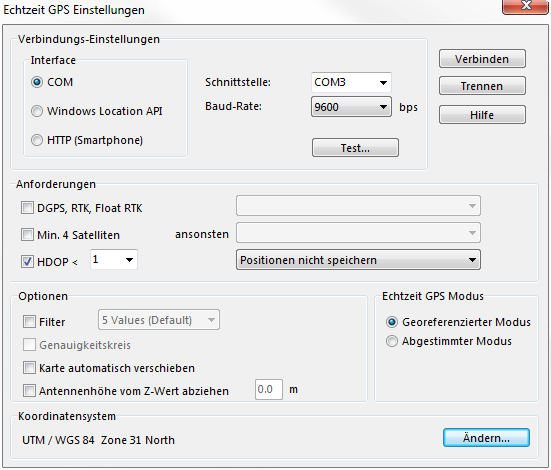
Echtzeit GPS Einstellungen
Verbindungs-Einstellungen
Machen Sie folgende Verbindungs-Einstellungen für das GPS-Gerät:
- Schnittstelle: Wählen Sie den COM-Port über den das Gerät mit dem Computer verbunden ist.
- Echtzeit Geschwindigkeit: Wählen Sie die Geschwindigkeit. NMEA 0183 ist üblicherweise 4800 bps aber einige Geräte senden ihre Daten mit einer anderen Geschwindigkeit.
- Klicken Sie die Schaltfläche Test... um den Dialog GPS testen anzuzeigen. Die vom GPS-Gerät empfangenen NMEA-Signale werden hier angezeigt und die Verbindung kann so überprüft werden.
Anforderungen
Folgende Anforderungen können definiert werden:
- DGPS, RTK, Float RTK: Wählen Sie diese Option um DGPS, RTK, Float RTK zu nutzen und definieren Sie ob Messwerte ohne DGPS, RTK, Float RTK gelten soll Positionen nicht speichern oder Positionen nicht speichern und nicht anzeigen.
 Diese Option wirkt sich nur dann aus, wenn das GGA-Signal übertragen wird. Klicken Sie die Schaltfläche Test... um zu schauen welches Signal übertragen wird.
Diese Option wirkt sich nur dann aus, wenn das GGA-Signal übertragen wird. Klicken Sie die Schaltfläche Test... um zu schauen welches Signal übertragen wird.
- Min. 4 Satelliten: Wählen Sie diese Option als Genauigkeits-Anforderungrement und definieren Sie was für Messwerte gelten soll, die mit weniger als 4 Satelliten berechnet wurden: Positionen nicht speichern oder Positionen nicht speichern und nicht anzeigen.
 Diese Option wirkt sich nur dann aus, wenn das GGA-Signal übertragen wird. Klicken Sie die Schaltfläche Test... um zu schauen welches Signal übertragen wird.
Diese Option wirkt sich nur dann aus, wenn das GGA-Signal übertragen wird. Klicken Sie die Schaltfläche Test... um zu schauen welches Signal übertragen wird.
- HDOP: Wählen Sie diese Option um eine Obergrenze für die HDOP (Horizontal Dilution of Precision) festzulegen und definieren Sie was für Messwerte mit einer höheren HDOP gelten soll: Positionen nicht speichern oder Positionen nicht speichern und nicht anzeigen.
Optionen
- Filter: Wählen Sie diese Option um den Filter zu aktivieren und bestimmen Sie wieviele GPS-Positionen gemittelt werden sollen. Daraus resultieren genauere Werte, welche allerdings langsamer aktualisiert werden.
- Genauigkeitskreis: Diese Option ist verfügbar, wenn der Filter aktiviert ist. Wählen Sie diese Option um den Genauigkeitskreis anzuzeigen. Er zeigt die Genauigkeit der letzten 5 Messungen mit einem Kreis um die GPS-Markierung an.
- Automatisches Verschieben der Karte: Wählen Sie diese Option um das Kartenfenster automatisch zu verschieben, falls die GPS-Markierung an den Rand stösst.
- Antennenhöhe vom Z-Wert abziehen: Wählen Sie diese Option um den Z-Wert zu korrigieren. Der eingegebene Wert wird vom gemessenen Wert abgezogen.
- Echtzeit GPS Modus: Wählen Sie zwischen Georeferenzierter Modus (seit OCAD 9) und Abgestimmter Modus (bis OCAD 8).
- Koordinatensystem: Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche Ändern... um das Koordinatensystem zu ändern. Der Dialog Koordinatensystem wird angezeigt.
Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche OK um Echtzeit GPS einzuschalten. Die GPS-Box wird in der rechten unteren Ecke von OCAD angezeigt, falls das GPS-Gerät korrekt mit OCAD verbunden ist.
Schliessen Sie den Dialog Echtzeit GPS Einstellungen oder klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche Abbrechen um Echtzeit GPS auszuschalten.
GPS testen
Klicken Sie die Schaltfläche Test... im Dialog Echtzeit GPS Einstellungen um das Fenster GPS testen anzuzeigen.
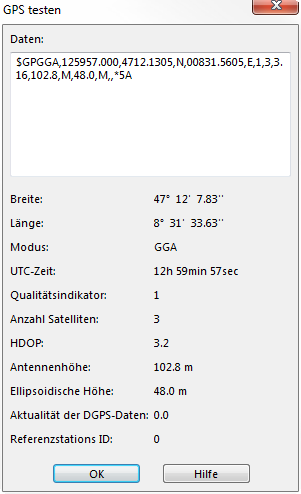
Die von OCAD empfangenen GGA-Signale werden im Feld Schnittstellen-Daten angezeigt. Die Zeichen 4 bis 6 zeigen die Abkürzung GGA (z.B. $XXGGA...). RMC-Signale werden angezeigt, wenn OCAD keine GGA-Signale empfängt. RMC-Signale enthalten keine Informationen über DPGS und die Anzahl Satelliten. Die Messwerte können trotzdem von OCAD verwendet werden. Das Feld Schnittstellen-Daten bleibt leer wenn das GPS-Gerät andere als die beiden beschriebenen Signale sendet oder wenn ein Verbindungsproblem besteht. Überprüfen Sie ob unter Echtzeit GPS Einstellungen der richtige COM-Port eingestellt ist und ob das GPS-Gerät korrekt mit dem PC verbunden ist.
GGA Beispielsignal:
$GPGGA,092750.000,5321.6802,N,00630.3372,W,1,8,1.03,61.7,M,55.2,M,,*76
RMC Beispielsignal:
$GPRMC,092750.000,A,5321.6802,N,00630.3372,W,0.02,31.66,280511,,,A*43
Kartieren mit Echtzeit GPS
Die GPS-Box wird in der rechten unteren Ecke von OCAD angezeigt, falls das GPS-Gerät korrekt mit OCAD verbunden ist.

Folgende Informationen werden in der GPS-Box angezeigt:
- Ostwert: Hier wird der Koordinaten-Ostwert angezeigt. Falls der Filter aktiviert ist, der gemittelte Wert.
- Nordwert: Hier wird der Koordinaten-Nordwert angezeigt. Falls der Filter aktiviert ist, der gemittelte Wert.
- Höhe: Hier wird die Höhe angezeigt. Falls der Filter aktiviert ist, der gemittelte Wert.
- DGPS: Ein grüner oder roter Punkt zeigt an ob ein DGPS-Signal empfangen wird.
- Satelliten: Hier wird der Koordinaten-Ostwert angezeigt. Falls der Filter aktiviert ist, der gemittelte Wert.
- Nordwert: Die Anzahl empfangener Satelliten wird hier angezeigt.
- HDOP: Die HDOP (Horizontal Dilution of Precision) wird hier angezeigt. HDOP ist ein Qualitätsindikator für die Positionsdaten der sichtbaren Satelliten. HDOP-Werte unter 4 sind sehr gut, HDOP-Wert grösser 8 sind schlecht.
- Genauigkeit (x Val): Hier wird die Genauigkeit (root mean square) für eine bestimmte Anzahl letzter Messungen angezeigt. Die Anzahl wird über die Filter-Länge in den Echtzeit GPS Einstellungen definiert.
Unterhalb des Informationsbereichs der GPS-Box hat es mehrere Schaltfächen:
Start GPS-Messung: Click this icon to create an OCAD object with the receiving GPS information. A symbol must be selected. Choose a point symbol and click the Start GPS Measurement icon to create an object at the position of the GPS marker. If a line or area symbol is selected, OCAD starts with the measurement and draws a vertice for every recieved position. The object is represented with a thin black line.
GPS-Messung unterbrechen: Click this icon to interrupt the GPS measurement without finishing the object. Click the icon again to continue with the measurement.
Stop GPS-Messung: Click this icon to finish the line or area object. The object is displayed with the assigned symbol.
GPS-Marke suchen: Click this icon to move the view to the GPS marker. Enable the Auto Scroll option to always move the view, when the GPS marker is leaving the current view.
Filter: Turn on or off the filter by clicking this icon. The filter can be adjusted in the Real Time GPS Settings dialog.
Genauigkeitskreis: Turn on or off the accuracy circle by clicking this icon. This shows the accuracy of the last 5 measurements with a circle around the GPS marker. This option is only available when the Filter is enabled.
- Select Vertex Type: In this dropdown list you can select between two types of Vertices:
- Choose the Normal Vertex option when a point should be added to the object for every position received from the GPS device.
- Choose the Corner Vertex option when a position should be manually added to the object by clicking the
Start GPS Measurement button. This option is typically used to draw objects with straight parts and corners like a fence. If a point or text object is selected, the vertex type cannot be changed.
Add GPS Position to Calculate Average: Click this button for every position you want include into an average calculation. The number of added positions is shown in the button hint. Click the
Start GPS Measurement icon to create the object at the calculated average position. This function is only available when a point symbol is selected. This is especially useful when the GPS position of an uncrossable feature (e.g. small house, deep hole, huge tree etc.) is to be measured. Some points around the feature have to be recorded and by clicking the
Start GPS Measurement icon, the average point can be found.
Open Real Time GPS Settings: This icon opens the Real Time GPS Settings dialog box.
![]() The GPS cursor is drawn with the mark color. Change the Mark Color in the Drawing and Editing part of the OCAD Preferences.
The GPS cursor is drawn with the mark color. Change the Mark Color in the Drawing and Editing part of the OCAD Preferences.
Adjust GPS 


This command is activated when the Real Time GPS is turned on and the Adjusted mode is set in the Real Time GPS Settings dialog box.
Choose this command to adjust your base map to the coordinates provided by the GPS. The Adjust GPS dialog box is displayed.
You can use up to 32 points for the adjustment. The existing adjustment points are listed in the Adjust points box.
Note: You can turn on or off each adjustment point by checking it or not.
The dialog provides the following functions:
- Close: Close the dialog box by clicking this button. The Adjust GPS dialog is a non-modal dialog.
- New: You can create a new adjustment point when you are at a known position in the terrain and your GPS device sends the position. Click this button and the cursor changes to a satellite symbol. Mark your position on the base map. The point is added to the adjustment points and the adjustment is recalculated.
- Rename: Click this button to rename the selected adjustment point.
- Delete: Click this button to delete the selected adjustment point.
- Angle: If you use only one adjustment point, you can enter the angle of your map here. You must enter the angle of your map compared to the WGS84 coordinate system used by the GPS device. The angle of the WGS84 coordinate system is normally different from your country’s coordinate system. If the map is rotated counterclockwise, enter a positive angle otherwise enter a negative angle.
If more than one adjustment point is used, the angle is calculated from the adjustment points. In this case the Angle value is not used.
Import Data from GPS Device 


This function is obsolete! If you want to import GPS data from GPS devices, import the waypoints and tracks with the corresponding software of the GPS device to the computer. Then use the Import from File function in OCAD. As an alternative, for fieldwork, use the Real Time GPS function.
Choose this command to import tracks or waypoints from a GPS Garmin eTrex device. The GPS device must be connected to the PC with a serial data cable or Bluetooth.
- GPS: In this field the information about the GPS device is displayed.
- Status: In this field the status between OCAD and GPS is displayed.
Connection
- Connect GPS: Click this button to connect OCAD with the GPS device. After a successful connection the GPS information and the status are displayed.
- Settings: Click this button to change the GPS settings. The Import from GPS Settings dialog is displayed.
GPS data
- Get waypoints: Click this button to load all waypoints. Each waypoint is displayed with in a row in the GPS data field.
- Get tracks: Click this button to download all tracks. Each track is displayed with in a row in the GPS data field. Only the start point is displayed.
![]() This command can take several minutes!
This command can take several minutes!
OCAD objects
- Set labels: Check this option to create also text objects with the name of the waypoints and tracks.
- CRT: Use a Cross Reference Table to assign symbols to the waypoints and tracks. OCAD creates Unsymbolized Objects if no Cross Reference Table is selected.
- Each line of the cross reference table contains the OCAD symbol number and the Garmin symbol name.
- Example of a cross reference table:
535.0 waypoint dot 536.0 campground symbol 540.0 scenic area symbol
- Create: Select the waypoints and tracks in the GPS data field and click this button to create OCAD objects from the selected GPS data.
![]() A popup menu appears when clicking the list with the GPS data with the right mouse button. In this popup menu you have the option to Select all, Unselect all and Clear list. With the Clear list command all waypoints and tracks are removed. In addition, you can Make an OCAD object. By clicking this command, an OCAD object of the selected track or waypoint is created.
A popup menu appears when clicking the list with the GPS data with the right mouse button. In this popup menu you have the option to Select all, Unselect all and Clear list. With the Clear list command all waypoints and tracks are removed. In addition, you can Make an OCAD object. By clicking this command, an OCAD object of the selected track or waypoint is created.
Import from GPS Settings
In this dialog box you can make the setting for the GPS data import. Verify also your settings on the GPS device (e.g. data format: GARMIN)!
- Port: Choose the port where the GPS device is connected.
- Speed data import: Choose the speed of the serial port. Garmin defines 9600 bps.
- Coordinate system: Click the Change button to select or change the coordinate system. The Coordinate System dialog box appears.
Import from File 




Choose this command from the GPS menu to import a GPS data file to the current map. The Load GPS data from files dialog box is displayed. Initially all importable GPS data files are listed. The following file types can be imported:
- GPX files
- FRWD files
- NMEA files
The Import from File dialog appears, where all available waypoints and tracks from the imported file are listed. There are several options in the OCAD objects part of the dialog:
- Set label: Check this option to create also text objects with the name of the waypoints and tracks.
- Assign Symbols: Check this option to assign a specified symbol to the imported objects. Otherwise OCAD will create Unsymbolized Objects.
- CRT: Use a Cross Reference Table to assign symbols to the waypoints and tracks.
![]() A popup menu appears when clicking the list with the GPS data with the right mouse button. In this popup menu you have the option to Select all, Unselect all and Clear list. With the Clear list command all waypoints and tracks are removed. In addition, you can Make an OCAD object. By clicking this command, an OCAD object of the selected track or waypoint is created.
A popup menu appears when clicking the list with the GPS data with the right mouse button. In this popup menu you have the option to Select all, Unselect all and Clear list. With the Clear list command all waypoints and tracks are removed. In addition, you can Make an OCAD object. By clicking this command, an OCAD object of the selected track or waypoint is created.
Click the Import button to import all selected tracks or waypoints in the list.
GPS Map Offset
This dialog box appears if the GPS coordinates are out of the maximum map size. Adjust the following parameters:
- Coordinate system If you work with GPS you must select a coordinate system. Click the Change button to select or change the coordinate system. The Coordinate System dialog box appears.
- Offset Choose here whether you want to change the OCAD real world coordinates or to keep the existing ones.
- New offset: Choose this option if no real world coordinates are defined for the map. OCAD already proposes reasonable values. You can leave theme unchanged.
- Existing offset and angle: Choose this option if the map already has real world coordinates and you want to fit the imported objects to the existing coordinates.
Laser Distance Meter 

Read more about using the "TruPulse 360/360B" Laser Range Finder on the Laser Distance Meter page.
Previous Chapter: DEM
Next Chapter: Database
Back to the Main Page.