Map Transform
Move 



Select the Transform item in the Map menu and choose Move.
The Move Map dialog appears. Depending on wheter you are using paper coordinates or real world coordinates (Set Scale and Coordinate System) you can enter different values.
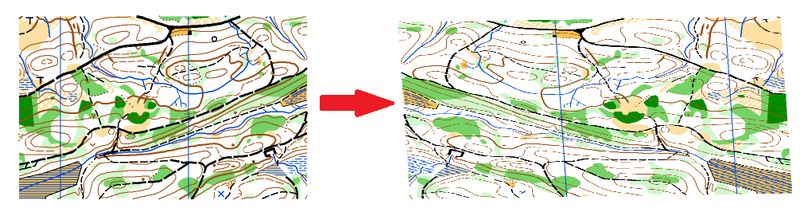
With set paper coordinates enter a X and a Y value in mm. By clicking the OK button the map is moved in the desired direction.
With set real world coordinates enter a value in m for easting and northing. By clicking the OK button the map is moved in the desired direction.
Check the corresponding option to move also Background Maps, Layout Objects and Bookmarks.
![]() Do not use this dialog to change the real world coordinate offset if the map is georeferenced. To move a georeferenced map, use the Center Map to Drawing Area function in the Transform submenu of the Map menu and enter the new offset.
Do not use this dialog to change the real world coordinate offset if the map is georeferenced. To move a georeferenced map, use the Center Map to Drawing Area function in the Transform submenu of the Map menu and enter the new offset.
Stretch or Shrink 




Select the Transform item in the Map menu and choose Stretch/Shrink.
The Stretch/Shrink Map dialog opens.
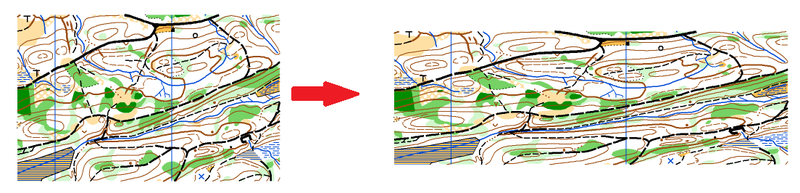
Enter a percentage value for the horizontal strech/shrink and the vertical stretch/shrink. If both values are the same, the proportions of the map are kept.
Check the corresponding boxes if you want to reflect the map horizontally or vertically.
Click the OK button when you are finished.
Mirror 




Select the Transform item in the Map menu and choose Mirror.
The Mirror Map dialog opens, which is the same as the Stretch/Shrink Map dialog.
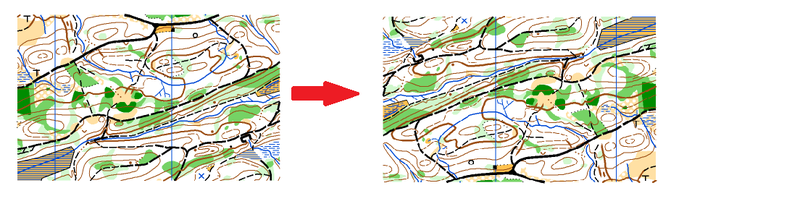
Enter a percentage value for the horizontal strech/shrink and the vertical stretch/shrink. If both values are the same, the proportions of the map are kept.
Check the corresponding boxes if you want to reflect the map horizontally or vertically.
Click the OK button when you are finished.
Rotate Map 




Select the Transform item in the Map menu and choose Rotate Map.
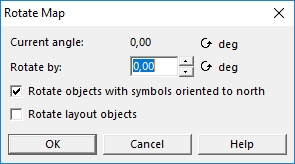
The Rotate Map dialog opens.
Enter an angle in degrees and check the option Rotate objects with symbols orientated to north if yout want the symbols stay orientated to north when you use the Rotate function.
![]() To consider the declination and rotate map to magnetic north, use the function Rotate Map to Magnetic North, which is more sophisticated than the function Rotate Map.
To consider the declination and rotate map to magnetic north, use the function Rotate Map to Magnetic North, which is more sophisticated than the function Rotate Map.
![]() Select a Point or Line Symbol and go to the symbol diaglog (Symbol>Edit) and see that the option Orientated to north when rotating the map is checked for that particular symbol.
Select a Point or Line Symbol and go to the symbol diaglog (Symbol>Edit) and see that the option Orientated to north when rotating the map is checked for that particular symbol.
Check Rotate layout objects and your layout objects will be rotated as well.
Layout images will not be rotated.
Click the OK button to finish.
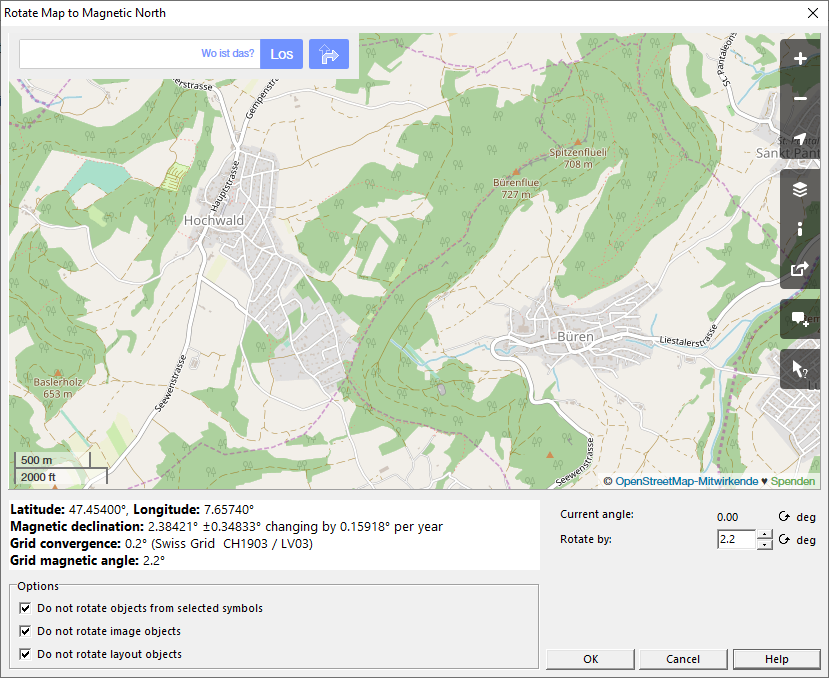
Rotate Map to Magnetic North 




This function helps you to rotate your map so that magnetic north points straight up.
To do so, the function opens Open Street Map at your current position. It takes two values into consideration:
- Magnetic declination: The angle between the direction of the magnetic meridians and the direction to the geographic North Pole at the observation site.
- Grid convergence: The angle at the observation site between true north and grid north.
- Grid magnetic angle: The sum of the two values above, by how much the map should be rotated.
![]() If you want to know more about declination, we can recommend our OCAD blog.
If you want to know more about declination, we can recommend our OCAD blog.
- Current angle: The current angle of your map.
- Rotate by: By default, it is the value from the Grid magnetic angle field. You can adjust it manually if you wish.
- Example: Current angle of your map is 0°, Grid magnetic angle is 2.1° and is supposed to change +0.12° per year. It would be an option to rotate the map by 2.6°. In this case, the deviation of your map would not be more than 0.5° for the next 8 years.
Click the OK button and your map will be aligned to magnetic north.
Options
- Do not rotate objects from selected symbols: You may not want to rotate certain objects, e.g. texts or symbols you use for the layout. Select these symbols beforehand in the Symbol box. Hold the Shift and/or Ctrl key for multiple selection.
- Do not rotate image objects: Set this option active, if you do not want to rotate image objects.
- Do not rotate layout objects: Set this option active, if you do not want to rotate layout objects.
![]() Your map has to be georeferenced and a Coordinate System has to been set to use this function.
Your map has to be georeferenced and a Coordinate System has to been set to use this function.
![]() If the web service is not available, plese see here.
If the web service is not available, plese see here.
![]() In the Map Menu, there are two more functions where you could rotate your map:
In the Map Menu, there are two more functions where you could rotate your map:
- Set Scale and Coordinate System: Do not edit the Angle in the function Set Scale and Coordinate System. Only change the angle there, if you start a new map and haven't drawn any objects yet.
- Rotate Map: The function Rotate Map is basically the same as Rotate Map to Magnetic North, but not that sophisticated.
Change Coordinate System 


Select the Transform item in the Map menu and choose Change Coordinate System.
The Change Coordinate System dialog opens.
The current coordinate system is displayed in the Change map from part of the dialog.
Click the Choose button in the Into part to choose a new coordinate system. Select the system in the Coordinate System dialog and click the OK button.
The new offset is displayed in the Horizontal offset and Vertical offset fields and can be edited there, too.
The option Scale symbols is only enabled when Google Mercator coordinate system is choosen. If this option is checked then OCAD scales all symbols according to the new scale in the center of the map. The map looks similar as before the transformation.
Click the OK button when finished. OCAD converts every vertex' coordinate to UTM and then (if necessary) to the desired coordinate system. Due to different origins of the coordinate systems the map gets transformed (stretched/shrinked and rotated).
Affine 


Select the Transform item in the Map menu and choose Affine to adjust the whole map on background map or on grid. With this function you can geo-reference the map. The grid button must be pressed to see the grid. You can use 1 to 12 points for the adjustment. For each point you do the following:
- Mark a point on map.
- Mark the same grid point on reference (background map or grid).
When you have adjusted enough points, press the Enter key on the keyboard. The map is rotated and stretched (Affine transformation) to get the best fit for the adjustment points. You can achieve a precise adjustment with 4 adjustment points arranged in a rectangle. In this way you can compensate rotation and distortion. The horizontal and vertical scales will be adjusted individually.
![]() This function works in the same way as the Adjust a Background Map function, but it is for the map.
This function works in the same way as the Adjust a Background Map function, but it is for the map.
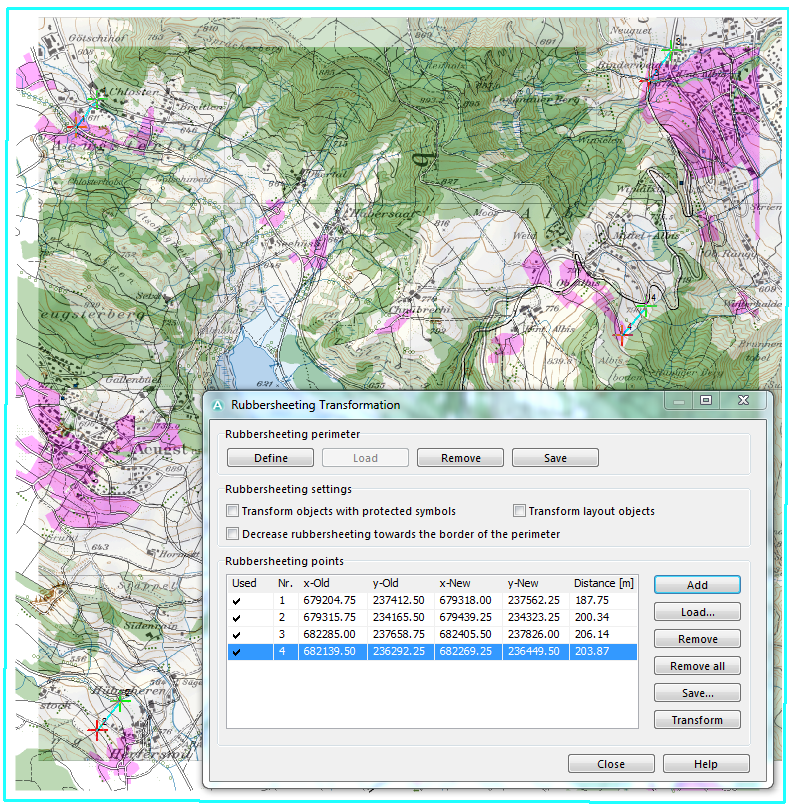
Rubbersheeting 


Select the Transform item in the Map menu and choose Rubbersheeting to adjust the map or a part of the map to a geo-referenced background map. The Rubbersheeting Transformation dialog appears.
Rubbersheeting perimeter
The Rubbersheeting perimeter is an area in which the Rubbersheeting Transformation is carried out. Objects outside of the rubbersheeting perimeter are not transformed.
Click the Define button and define the perimeter by drawing a polyline on the map (one corner per click). To define a new rubbersheeting perimeter click the Remove button to remove the actual one. Click the Load button to load an exported rubbersheeting perimeter (txt-File). Click the Save button to save the current perimeter.
Rubbersheeting settings
Check the corresponding boxes if you want to transform objects with protected symbols, transform layout objects or decrease rubbersheeting towards the border of the perimeter.
Rubbersheeting points
Click the Add button and do the following steps:
- Click a point on the map.
- Click the same point on the reference map (grid or background map). The rubbersheeting points are shown on the map by a red and a green cross and a connection line.
- Do the same procedure for other points.
- Click the Transform button to transform the map. Click the Save button to save the rubbersheeting points. Click the Remove button to remove the selected rubbersheeting point. Click the Remove all button to remove all rubbersheeting points. Click the Load button to load a saved selection of rubbersheeting points.
Click the Close button when finished.
![]() -Click the Undo button in the Standard Toolbar if you are not satisfied with the rubbersheeting transformation.
-Click the Undo button in the Standard Toolbar if you are not satisfied with the rubbersheeting transformation.
- -Uncheck rubbersheeting points in the Used column if they should not be included in the transformation. Unchecked rubbersheeting points appear in gray color on the map.
- -The rubbersheeting perimeter defines that only objects or vertices of objects within this perimeter are transformed. But it is possible that objects or vertices of objects are moved out of the perimeter by the transformation! Place rubbersheeting point pairs with the same position on the perimeter border to avoid this.
- -The Affine function is much easier to handle and gives more or less the same result.
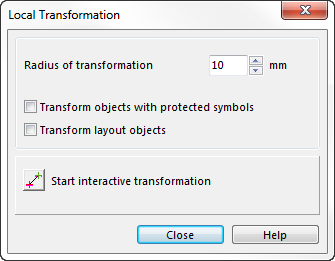
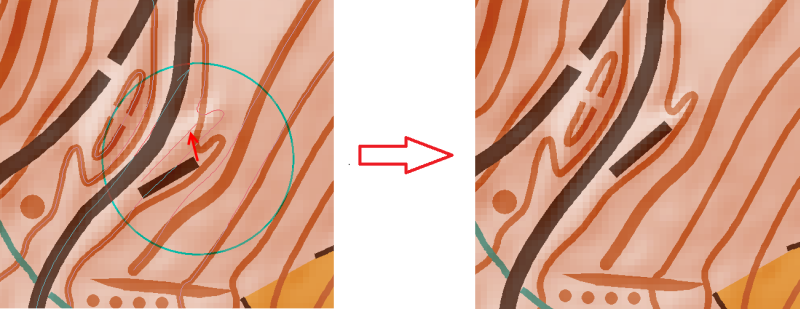
Local Transformation
Local Transformation is an interactive tool to eliminate local distortions. This tool makes the adjustment of existing maps to geo-referenced base maps (hillshading, orthophotos etc.) easier and more accurate too.
Select the Transform item in the Map menu and choose Local Transformation to open the Local Transformation dialog.
- Define the Radius of transformation.
- Choose if objects with protected symbol and layout objects shall be transformed as well.
- Click on the Start the interactive transformation button.
- Press the left mouse button at the transformation center and move the mouse meanwhile to transform. The mouse up needs to be within the circle.
 While pressing the left mouse button, the beforehand defined transformation radius will be shown with a blue circle.
While pressing the left mouse button, the beforehand defined transformation radius will be shown with a blue circle. Each vertex inside the circle will be transformed. Thus the transformation doesn't stop exactly at the border of the circle for line and area objects that are partially within the circle. They get transformed until their first vertex out of the circle.
Each vertex inside the circle will be transformed. Thus the transformation doesn't stop exactly at the border of the circle for line and area objects that are partially within the circle. They get transformed until their first vertex out of the circle. It is possible to edit the map while having opened the non-modal Local Transformation dialog.
It is possible to edit the map while having opened the non-modal Local Transformation dialog.
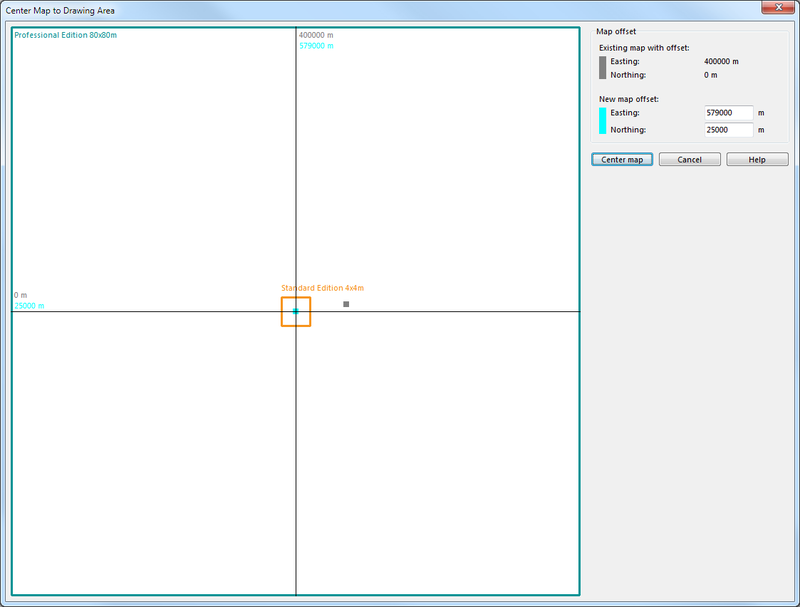
Center Map in Drawing Area 


Select the Transform item in the Map menu and choose Center Map in Drawing Area. The Center Map in Drawing Area dialog appears.
This function is often used to center a map drawn in OCAD Mapping Solution edition into the smaller drawing area from OCAD Orienteering, Starter or CS edition. OCAD moves the map offset, all objects, all background maps and all bookmarks. After this function the map is still geo-referenced. In the dialog the extent with the existing map offset is shown in grey, the extent with the new offset in blue. The green rectangle shows the drawing area of OCAD Mapping Solution edition (80x80m), the orange the drawing area from Orienteering, Starter and CS edition (4x4m). If a map should be visible in all OCAD editions then the entire map must fit in the 4x4m drawing area.
The proposed new map offset is displayed in the New map offset fields and can be edited there. This new map offset is calculated from the map and his visible background maps. If the background maps are hidden then OCAD calculates the new map offset only from the map.
![]() Look for area symbols with a hatching structure (e.g. north lines) that have been cut out to make underlying objects visible. For an ISOM 2017 1:10'000 map, the hatch for north lines area symbol has a distance of 30mm, which is 300m in reality. If you center the map to the drawing area, you should adjust the suggested offset so it is divisible by 300m, e.g. 3km. (Example: Existing offset: 619000, Suggested New Offset: 612000, Adjust Offset to: 613000).
After the transformation the map is not excalty centered, but all area structures with hatch distance divisible by 300m remain the same.
Look for area symbols with a hatching structure (e.g. north lines) that have been cut out to make underlying objects visible. For an ISOM 2017 1:10'000 map, the hatch for north lines area symbol has a distance of 30mm, which is 300m in reality. If you center the map to the drawing area, you should adjust the suggested offset so it is divisible by 300m, e.g. 3km. (Example: Existing offset: 619000, Suggested New Offset: 612000, Adjust Offset to: 613000).
After the transformation the map is not excalty centered, but all area structures with hatch distance divisible by 300m remain the same.
Click the Center map button to move the map to the center of the drawing area.
The geo-reference of the map is not changed.
Back to the Map page.